New data prove:
Tridectin is the most powerful tool for worm control. Regional data. Best reflect the status in your region. Drench decision is easy now.
- Offers 99% average efficacy!
- More effective than Abamectin-Triples
- More effective against Barber’s Pole worm than Closantel-combinations
- At least as efficacious as Monepantel/Derquantel combinations
- Proven by reliable data, collected in 2018 and 2022 all across Australia
- Most precise reflection of the current situation in the field
- Makes drench decision easy. And secures your sheep business.
Tridectin controls even Abamectin-triple-resistant worms
-
Heading 1
Resistance grows - So selecting the right drench is key
- Resistance is increasing all over Australia and reduces profit of your sheep farm
- Resistance means worms are not being killed by active ingredients of sheep drenches any more. The more worms survive your treatment the higher the infection pressure on your property gets, affecting the health of your sheep flock.
- Virbac put lots of effort into generating new FECRT data in order to help you selecting the right drench for your property
- We help you to better control resistance on your property. Because we care about your animals. We think sustainably. We want to secure your farm business now and in the future.
We offer the most recent data - Why is that so important?
- These data have been collected over the past 3 years. Drench tests should be repeated every 3-5 years to ensure we choose drench actives that properly control the worms on the farm today. It is important to know the resistance status on your farm as the worm population on the neighbour’s farm might be totally different.
What has been tested?
-
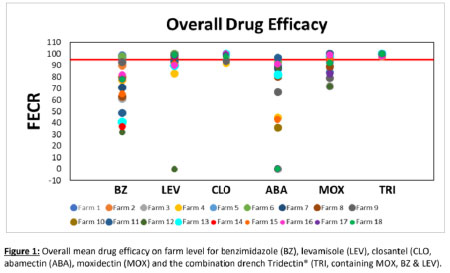
Faecal Egg Count Reduction Tests (FECRTs) have been collected all over Australia:
- 74 different farms have been tested so far
- Average sheep flock size
- Efficacy of the main products used in the field was tested
- Get more information on the importance of, and how to conduct a drench test by following this link to the wormboss web page: Testing drench effectiveness with a DrenchTest
-
Heading 2
Strong persistent action against Barber’s Pole worm:
- Ensured by the unique micellar formulation
- Tridectin offers persistent activity against Barber’s Pole worm and Small Brown Stomach Worm for 14 days!
- Tridectin has the longest-lasting effect among all products. Proven by registration and by current data from the field.
- Significantly reduces infection pressure on your property. Pastures are less contaminated. This offers a strong control of Barber’s Pole worm, even in heavily infested regions.
Moxidectin ensures sustainable worm control:
- It helps to protect the efficacy of other actives (e.g. Monepantel, Derquantel)
- As Abamectin-based products have been widely used, resistance against Abamectin has massively increased (which our new data clearly demonstrate)1,2
- A rotating use including all actives that are proven to work on your property is therefore recommended and should be the basis for your worm management program.
- Tridectin ensures the future effectiveness of your drench programme - and your business.
Makes drenching flexible and convenient:
- Can be used for ewes (including pregnant or lactating ewes), lambs and rams - at any time of the year
- Tridectin is a key component and fits into every drench programme
-
Offers high flexibility through very short withholding periods:
- WHP Meat: 7 days
- ESI: 17 days
- Improves marketing options for your sheep
NATIONAL AVERAGES
Overall Efficacy
Moxidectin + White + Clear Drench
Monepantel
Derquantel & Abamectin
Abamectin + White + Clear Drench (Aba-Triple)
Abamectin + White + Clear Drench + Closantel
Abamectin
Broad spectrum
Overall National Efficacy Rates
Barber’s Pole Worm
National Efficacy Rates
Black scour worm
National Efficacy Rates
Brown stomach worm
National Efficacy Rates
Brown stomach worm
National Efficacy Rates
SELECT YOUR REGION
We make our data convenient for you:
- Our data are easy to understand
- We offer customized solutions
- Select the data you need by using different filters
- Selecting your regional data gives you a precise picture of the resistance status in your region. Management systems and worm populations differ from farm to farm. The results present the average efficacy of different actives and combinations in a region and not the situation on every farm.
- Drench tests should be performed every 3-5 years on every property to assist with selecting the appropriate drenches for that property.








- Western Australia Winter Rainfall
- South Australian Winter Rainfall
- Victorian Winter Rainfall
- Tasmania
- NSW Non-Seasonal Rainfall
- Qld/NSW Summer Rainfall/Slopes & Plains
- Qld/NSW Summer Rainfall/Tablelands & Slopes
- Pastoral Region
Western Australian Winter Rainfall
The South-West Medium to High Rainfall Zone
This includes the corner of the state, south-west of the 350 mm rainfall isohyet. It starts at the coast a little north of Kalbarri, continues west of Mullewa and Perenjori, then includes Cadoux, Quairading, Corrigin, Lake Grace, Ravensthorpe, and Esperance near its eastern or northern edge.
Sheep are a more important part of the farming enterprise than in districts to the east, and both the total rainfall and seasonal duration (months of rainfall) is greater in this zone. Conditions for worm burden development are therefore more favourable than in drier areas.
There is a large variation between districts in this zone in the annual risk of significant worm problems due to rainfall differences, although the basic control plan is applicable. The worm risk is lower east of the 500 mm isohyet, where there is usually a shorter pasture growth season and a greater area of the farm is under crop.
Closer to the coast within the zone the rainfall is considerably higher, and pastures often retain a green component over summer (a barber’s pole worm risk). Along the south coast and west of Bremer Bay, and in a coastal zone along the west coast as far as Geraldton, the rainfall is both greater and of longer seasonal duration, further increasing the likelihood and duration of the worm risk.
The Low Rainfall Cereal Zone
This zone is east of the 350 mm isohyet, extending to the border of the Pastoral Zone of the state and includes Mullewa, Wubin, Bullfinch, Southern Cross, Merredin, Hyden and Lake King. In these areas the summers are hot and the effective rainfall is relatively low. As cropping is the dominant enterprise, the large areas of crop stubbles provide significant opportunities to avoid worm intake. The worm risk is therefore low in most years, and especially in eastern areas of the zone, visible signs of worms are only occasionally seen after unusually heavy summer rainfall.
South Australian Winter Rainfall
The South-East zone
This zone is the south-eastern corner of the state below an approximate line running from Kingston SE to Bordertown, through to the Victorian border. The zone generally receives more than 550 mm annual rainfall. Although summers are warm, effective summer rainfall episodes (12mm or more) are not unusual, especially towards the coast. Pastures sometimes retain a substantial green component over summer.
The Higher Rainfall Mediterranean zone
This zone has the following areas:
- Kangaroo Island
- The southern tip of the Eyre Peninsula below Cummins
- Fleurieu Peninsula and the Adelaide Hills
- Clare Valley
Usually this zone receives more than 450 mm rainfall per year (though some areas are substantially higher) and summers are generally hot with no effective rainfall. Cropping can be a component of the enterprise mix.
The Lower Rainfall Mediterranean zone
This zone is north of the Higher Rainfall Mediterranean zone and extends to a line running from Ceduna across the Eyre Peninsula to between Cowell and Whyalla, then from around Port Pirie to south of Port Augusta, Orroroo and Peterborough, then east or north of Burra, Mannum, Karoonda to near Pinnaroo. This corresponds to Goyder’s line in many places.
Victorian Winter Rainfall
The area covers most of Victoria except for the drier north-western area (Mallee and northern Wimmera) to the north or west of Kaniva, Warracknabeal, Charlton and Cohuna. This area is in the WormBoss Pastoral region.
The more uniform- and summer-dominant rainfall areas of East Gippsland may also find the WormBoss NSW non-seasonal rainfall program a useful reference.
Tasmania
The Tasmanian high rainfall (prime-lamb) region
This region includes King Island, the North Coast between Wynyard and Launceston. These are the high winter rainfall areas with up to 1200 mm annually.
The Tasmanian medium to low rainfall (extensive) region
This region includes the north-east coast, the Midlands and Derwent Valley and the lower east coast. The rainfall is non-seasonal, between 350 and 600 mm annually.
The Tasmanian summer rainfall region
This region includes Flinders Island and in some years, the north-east coast. The medium to low rainfall region recommendations apply here, but the summer rainfall also predisposes to barber’s pole worms. Also, other areas in Tasmania with sheep on irrigated summer pastures may experience barber’s pole worm burdens in late summer and early autumn.
These boundaries are approximations only as seasonal temperature and rainfall variations affect worms.
Victorian Winter Rainfall
The area covers most of Victoria except for the drier north-western area (Mallee and northern Wimmera) to the north or west of Kaniva, Warracknabeal, Charlton and Cohuna. This area is in the WormBoss Pastoral region.
The more uniform- and summer-dominant rainfall areas of East Gippsland may also find the WormBoss NSW non-seasonal rainfall program a useful reference.
NSW Non-Seasonal Rainfall
The south western area (including the eastern Riverina) with hot summers and cool winters (includes the towns of Condobolin, West Wyalong, and Wagga Wagga).
The tablelands area with warm summers and cold frosty winters (includes the towns of Bathurst, Orange, Yass, Young, Goulburn, Cooma); and
The coastal area with warm to hot summers that are more humid and cool winters (includes the towns of Bega, Batemans Bay).
The eastern Riverina (includes the towns of Finlay, Narrandera and Griffith, Lockhart and Corowa) with hot summers and more winter rainfall dominance.
The region extends from an east-west line through Warren in the north to the NSW/Victoria border and west from the coast to a line from Nymagee (west of Nyngan and Tottenham) through to the Victorian border just west of Finlay.
Qld/NSW Summer Rainfall/Slopes and Plains
The southern and northern boundaries are lines running east-west through Warren, New South Wales and through Roma, Queensland, respectively. The eastern boundary runs north from Gilgandra (NSW) to Siding Springs just west of Coonabarabran, then through Narrabri, Yetman and Texas, then south of Warwick, and then along the range north to Kingaroy (Qld). The western border goes from Mitchell (Qld) in the north, to Bollon, Goodooga, and Brewarrina, ending between Nyngan and Cobar (NSW) in the south.
Other towns in this zone are Walgett, Coonamble, Wee Waa, Moree, Mungindi, Dirranbandi, St George, Goondiwindi, Inglewood, Moonee, Surat, Millmerran, Chinchilla, Dalby and Toowoomba.
Qld/NSW Summer Rainfall/Tablelands and Slopes
Mudgee, Dunedoo, Merriwa, Coolah, Tamworth, Coonabarabran, Narrabri, Gunnedah, Manilla, Barraba, Bingara, Bundarra, Inverell, Warialda, Walcha, Bendemeer, Uralla, Armidale, Guyra, Glen Innes, Tenterfield, Texas and Stanthorpe. Coastal towns included are Murwillumbah, Lismore, Grafton, Coffs Harbour, Port Macquarie, Muswellbrook, Maitland and their hinterland areas.
Pastoral Region
Queensland: north and west of Mitchell, and west of the Great Dividing Range to Hughenden, then west to Julia Creek, then south including Longreach and Charleville, and just including Windorah, Eromanga and Thargomindah in the south-west.
New South Wales: west of the following towns Goodooga, Nyngan, Lake Cargelligo, Griffith and Finley.
Victoria: north and west of an approximate line from Swan Hill across to Kaniva.
South Australia: north of Goyder’s line to the dingo fence.
Let’s go. Select your data.
Moxidectin + White + Clear Drench
SelectMonepantel
SelectDerquantel & Abamectin
SelectAbamectin + White + Clear Drench (Aba-Triple)
SelectAbamectin + White + Clear Drench + Closantel
SelectAbamectin
SelectMoxidectin Long Acting Injection
SelectMoxidectin Oral
SelectMonepantel & Abamectin
SelectClear Drench
SelectNaphthalophos
SelectWhite Drench
SelectClear + White Drench
SelectClosantel
SelectNaphthalophos + White Drench
SelectNaphthalophos + Clear + White Drench
SelectNaphthalophos + Clear Drench
SelectAbamectin + Closantel
SelectKEY
BenzimidazoleWhite Drench Levamisole Clear DrenchSELECTED DRENCHES - VICTORIAN WINTER RAINFALL
The area covers most of Victoria except for the drier north-western area (Mallee and northern Wimmera) to the north or west of Kaniva, Warracknabeal, Charlton and Cohuna. This area is in the WormBoss Pastoral region.
The more uniform-and summer-dominant rainfall areas of East Gippsland may also find the WormBoss NSW non-seasonal rainfall program a useful reference.